cervical compression constitute objective test serious injury|cervical injury surgical intervention : store In this classification, we recognize the three classic injury models: compression injury (Type A), anterior and posterior distraction injury (Type B), dislocation / translation . WEBOnlyFans is the social platform revolutionizing creator and fan connections. The site is inclusive of artists and content creators from all genres and allows them to monetize their content while developing authentic relationships with their fanbase. . The only non-essential cookies we use are for any personal referrals you make. We do not .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Grelha dos Programas do canal SPORT TV 1. Guia TV SPORT TV 1, filmes, horários e resumo dos programas de televisão. TudoNumClick. Menu MENU. Guia TV; Liga Futebol; Onde dá a Bola; Cinema; Euromilhões; . TRANSMISSÃO EM DIRETO. Transmissão do encontro a contar para a .
The objective of the initial evaluation of a patient with a suspected CSI is to identify the presence of injuries through thorough clinical and radiologic assessments as missed injuries are potentially catastrophic.
Objectives: Review the various types of cervical spine injuries and the pathophysiology accompanying each type. Summarize the relevant steps in performing an .
pathophysiology of cervical injuries
cervical spine testing procedure
Radicular pain in a young person is usually the result of a neurofibroma, while in the elderly it is commonly the result of compression by an osteophyte or invasion from secondary deposits in . high rate of missed cervical spine injuries due to: inadequate imaging of affected level. loss of consciousness. multisystem trauma. cervical spine injury necessitates careful . In this classification, we recognize the three classic injury models: compression injury (Type A), anterior and posterior distraction injury (Type B), dislocation / translation . Cervical column injuries include fractures, subluxation, dislocation, and ligamentous injuries. Early recognition and appropriate management can reduce the risk of .
Acute cervical spine trauma requires a high index of suspicion and thorough investigation to detect bone or ligament damage that can otherwise result in spinal cord injury. .The cervical spine is especially vulnerable to injury given the relative axial alignment of the facet joints, which require less force to dislocate compared with the thoracic or lumbar spine.This page provides a step-by-step overview of the key elements of the cervical spine evaluation, including the subjective assessment (history taking) and the objective assessment (observation and tests). It also introduces the .neck pain with radiating pain/cervical radiculopathy, including the upper limb tension test, Spurling's test, distraction test, and the Valsalva test. Cranial cervical flexion and neck flexor muscle endurance tests may be use in .
Cervical myelopathy is spinal cord compression in your cervical spine or neck. The most common type is cervical spondylotic myelopathy, which happens after natural changes to your body as you age. It can cause neck . Cervical myelopathy describes a spinal cord compression at the cervical level of the spinal column resulting in spasticity (sustained muscle contractions), hyperreflexia, pathologic reflexes, digit/hand clumsiness, or gait disturbance.[1][2][3] Classically, it has an insidious onset, progressing in a stepwise manner with functional decline. Without treatment, .These recommendations are based on expert opinion in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) best practice guide Assessment of neck pain [BMJ Best Practice, 2022b], a systematic review Manual Therapy in Cervical and Lumbar Radiculopathy [Kuligowski, 2021], expert opinion in narrative reviews Advances in the diagnosis and management of neck pain [Cohen, 2017], Cervical .
The objective of this study was to use flexibility tests to determine biomechanical instability of the cervical spine due to simulated axial compression injuries. . instability parameters indicated extension-compression injuries at the upper and middle cervical spine and flexion-compression injuries at the lower cervical spine. Increases in . Muscle spasms and neck stiffness are common to many cervical injuries and are non-specific findings that are routinely encountered, and do not constitute a positive test. The result of a positive Spurling test is a reproduction of cervical radiculopathy symptoms. Cervical radiculopathy can involve the neck, shoulder, or arm. The aim of this cross-sectional observational cohort study was to verify whether an objective and easily-used walk and run test is capable of detecting early gait impairment in a practical proportion of non-myelopathic degenerative cervical cord compression (NMDCC) patients and of revealing any correlation with severity of disability in DCM .
Cervical myelopathy is a form of myelopathy that involves compression of the spinal cord in the cervical spine (neck). Sterile fluids supply information Like many medical facilities across the nation, our supply chain is feeling the effects of Hurricane Helene’s aftermath.Hyperilexion injuries of the human cervical spine commonly occur in vehicular crashes, contact sports, diving, and falls. Flexion related injuries constitute a high percentage of all cervical spine injuries. The objective of this study was to determine the mechanisms and tolerance of the human cervical spine under hyperilexion loading This test is also known by other names, including the Foraminal Compression test and Spurling’s test. This test should not be used if a significant cervical injury is suspected. With the patient in the seated position, tilt and rotate the patient’s neck to the side of involvement. Cervical Myelopathy is a common form of neurologic impairment caused by compression of the cervical spinal cord most commonly due to degenerative cervical spondylosis. The condition most commonly presents in older patients with symmetric numbness and tingling in the extremities, hand clumsiness, and gait imbalance.
cervical spine cord test
Cervical radiculopathy can be difficult to diagnose, as many other neurological conditions, such as neuropathy, can cause pain and numbness. Because of this, you may need to undergo certain imaging tests so your healthcare provider can confirm a cervical radiculopathy diagnosis. What tests will be done to diagnose cervical radiculopathy?Cervical stenosis is one such degenerative condition that may affect the spinal cord and lead to compromised coordination of the extremities. When diagnosing cervical stenosis, doctors must determine whether progressive dysfunction (myelopathy) is present as a result of the spinal cord compression. See Cervical Stenosis with Myelopathy The Spurling test is used to help diagnose cervical radiculopathy. If you feel any pain during the test, it’s considered a positive result. This means you may have cervical radiculopathy. (2,3) The test is most commonly defined in current literature as passive cervical extension, ipsilateral rotation, and axial compression. (4) This summary contains information on use of the Spurling test in patients or clients .
The Cervical Spine. 136. Fig 7.1 • Reference of pain. Referred Local Pain Multisegmental Dural Segmental Multiradicular Monoradicular Soft tissue Bone. Fig 7.2 • Onset of pain. Onset Gradually Injury Serious pathology Soft tissue Non-specific Suddenly Articular Internal derangement Disc lesion Other condition Fracture/luxation Mechanical . “Cervical spondylosis,” sometimes called arthritis of the neck, is a general term for wear and tear that affects your cervical spine. If you have cervical spondylosis, your neck may ache, hurt or feel stiff. Healthcare .
Objective: To demonstrate the homogeneous causes and symptoms observed in patients with a concussion and patients with cervical injury and to provide information on clinical tests that can differentiate cervical injury from pathologic conditions of vestibular or central origin. . If symptoms increase with the test, cervical injury should be .
A fracture, or break, in one of the cervical vertebrae is commonly called a broken neck. Cervical fractures usually result from high-energy trauma, such as automobile crashes or falls. In elderly people, ground-level falls, such as falling off a chair, can result in a cervical fracture. Athletes are also at risk. A cervical fracture can occur if: Neck pain: CSS may cause chronic or intermittent neck pain.Pain levels and intensity may vary, and pain might radiate in the shoulders and arms. Arm pain and other arm symptoms: Nerve compression in the cervical spine can lead to pain in one arm or both sides. Additional arm symptoms include weakness, numbness, and tingling that might affect the hands. Find out what you need to know about the Hoffman test. Learn about the connection between the Hoffman sign, cervical cord compression, and cervical myelopathy.This protocol contains descriptions of various orthopedic tests applied to the cervical region. The following tests are included: • Arm Squeeze Test • Bakody’s Sign • Brachial Plexus Compression • Brachial Plexus Tension Test • Cervical Flexion (including Brudzinski’s Sign, Lhermitte’s sign, Lindner’s sign) • Cervical .


Compression fractures can happen to any part of your spine, but they usually occur in the thoracic spine (middle section). Osteoporosis is a common cause of compression fractures, in addition to trauma (like after an accident) or tumors that weaken the bone.. A healthcare provider may treat these fractures with medications, a back brace or surgery, .Examining people for signs of cervical radiculopathy. A combination of tests should be used to help identify cervical radiculopathy, including: The Spurling test. Arm squeeze test. Axial traction — a combination of a positive Spurling’s test, axial traction test, and arm squeeze test increases the likelihood of cervical radiculopathy. Cervical radiculopathy is most commonly precipitated by compression of a nerve root. Diagnosis is made by combining the patient’s symptoms, sensory and motor physical exam findings, and electrodiagnostic results. An electrodiagnostic evaluation may not be necessary if the clinical presentation is clear; however, electrodiagnostic studies confirm the diagnosis and .
The term "whiplash" injury was first coined by Harold Crowe in 1928 to define acceleration-deceleration injuries occurring to the cervical spine or neck region.[1] Later modified to an all-encompassing term known as whiplash-associated disorders (WAD), these clinical entities have been refined to describe any collection of neck-related symptoms following a .
cervical injury surgical intervention
Lemeunier N., da Silva-Oolup S., Chow N., et al. Reliability and validity of clinical tests to assess the anatomical integrity of the cervical spine in adults with neck pain and its associated disorders: Part 1-A systematic review from the Cervical Assessment and Diagnosis Research Evaluation (CADRE) Collaboration.
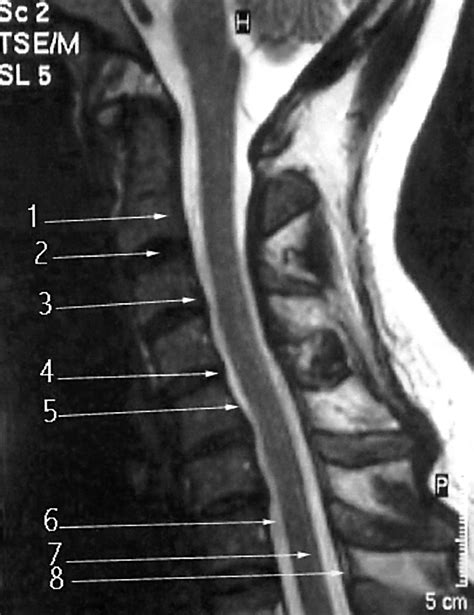
cervical injury lab tests
cervical injury diagnosis
cervical injury assessment protocol
5 de ago. de 2022 · Tudo o que você precisa saber sobre o jogo da 22ª rodada da Série B do Brasileiro
cervical compression constitute objective test serious injury|cervical injury surgical intervention